
Digital transformation will only grow in importance as we enter the near year as it allows organisations to leverage the power of digital technologies to fundamentally change how they operate and deliver value to customers. By embracing digital technologies, organisations can improve efficiency, increase competitiveness, and drive business growth.
In today’s fast-paced and rapidly changing business environment, digital transformation has become a necessity for organisations of all sizes and industries. With the proliferation of digital technologies, customers have come to expect seamless and personalised experiences, and organisations that are unable to meet these expectations are at risk of losing market share to competitors.
Yet, according to Forbes, the risk of failing your digital transformation is around 84%, and between 70% to 90% according to McKinsey, BCG, KPMG and Bain & Company, Source.
Many organisations still struggle with executing a digital strategy
Digital transformation is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful planning and execution. While it has the potential to drive significant business value and growth, it also carries significant risks and challenges. In order to succeed, organisations must carefully assess the risks and challenges and put in place the necessary resources and processes to ensure the success of the transformation.
Several common reasons why digital transformation efforts may fail, include the following;
- Lack of clear objectives and desired outcomes: Without a clear understanding of the business objectives and desired outcomes of the digital transformation effort, it is difficult to measure progress and ensure that the efforts are aligned with the overall goals of the organisation.
- Lack of leadership support and commitment: Digital transformation requires leadership support and commitment to be successful. Without this, it can be difficult to secure the necessary resources and drive the necessary changes throughout the organisation.
- Lack of a comprehensive and realistic plan: A comprehensive and realistic plan is essential for the successful execution of digital transformation. Without a plan that outlines the specific steps and resources required, it can be difficult to coordinate efforts and ensure that the transformation is on track.
- Insufficient communication and stakeholder engagement: Digital transformation often requires the collaboration and input of a wide range of stakeholders across the organisation. If these stakeholders are not adequately engaged and informed about the changes, it can be difficult to secure their buy-in and support.
- Resistance to change: Digital transformation often involves significant changes to processes, systems, and ways of working. Without a culture that is open to change and innovation, it can be difficult to drive the necessary changes throughout the organisation.
- Insufficient resources: Digital transformation requires the allocation of sufficient resources, including funding, personnel, and technology. Without these resources, it can be difficult to execute the transformation successfully.
Starting at the top, there first needs to be clear objectives and an ownership structure to follow
Effective digital transformation requires clear and well-defined objectives that are aligned with the overall business strategy of the organisation. By developing clear objectives, organisations can ensure that their transformation efforts are focused on achieving specific goals and outcomes, and that progress can be measured against these goals.
These can be both internal and external. Internal objectives are focused on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the organisation’s operations, while external objectives are focused on delivering value to customers and improving the organisation’s competitiveness in the market.
Examples of internal objectives might include streamlining business processes, improving the efficiency of internal communication and collaboration, or optimising the use of resources. External objectives might include improving customer satisfaction, increasing revenue or market share, or expanding the organisation’s reach into new markets.
They will need to be measured regularly and framed into KPI’s. Examples of this may include;
- Revenue growth: If the objective of the transformation is to drive revenue growth, a KPI might be the percentage increase in revenue over a specific period of time (e.g., year-over-year growth).
- Cost savings: If the objective is to reduce costs and improve efficiency, a KPI might be the percentage reduction in costs over a specific period of time (e.g., the first quarter after the transformation is implemented).
- Time to market: If the objective is to accelerate the development and launch of new products or services, a KPI might be the time it takes to bring a new product or service to market (e.g., the time from idea generation to market launch).
- Market share: If the objective is to increase the organisation’s share of the market, a KPI might be the percentage of the market served by the organisation (e.g., the percentage of total industry sales that the organisation captures).
- Customer acquisition: If the objective is to increase the number of customers served by the organisation, a KPI might be the number of new customers acquired over a specific period of time (e.g., the number of new customers acquired in the first quarter after the transformation is implemented).
Who owns the digital transformation?
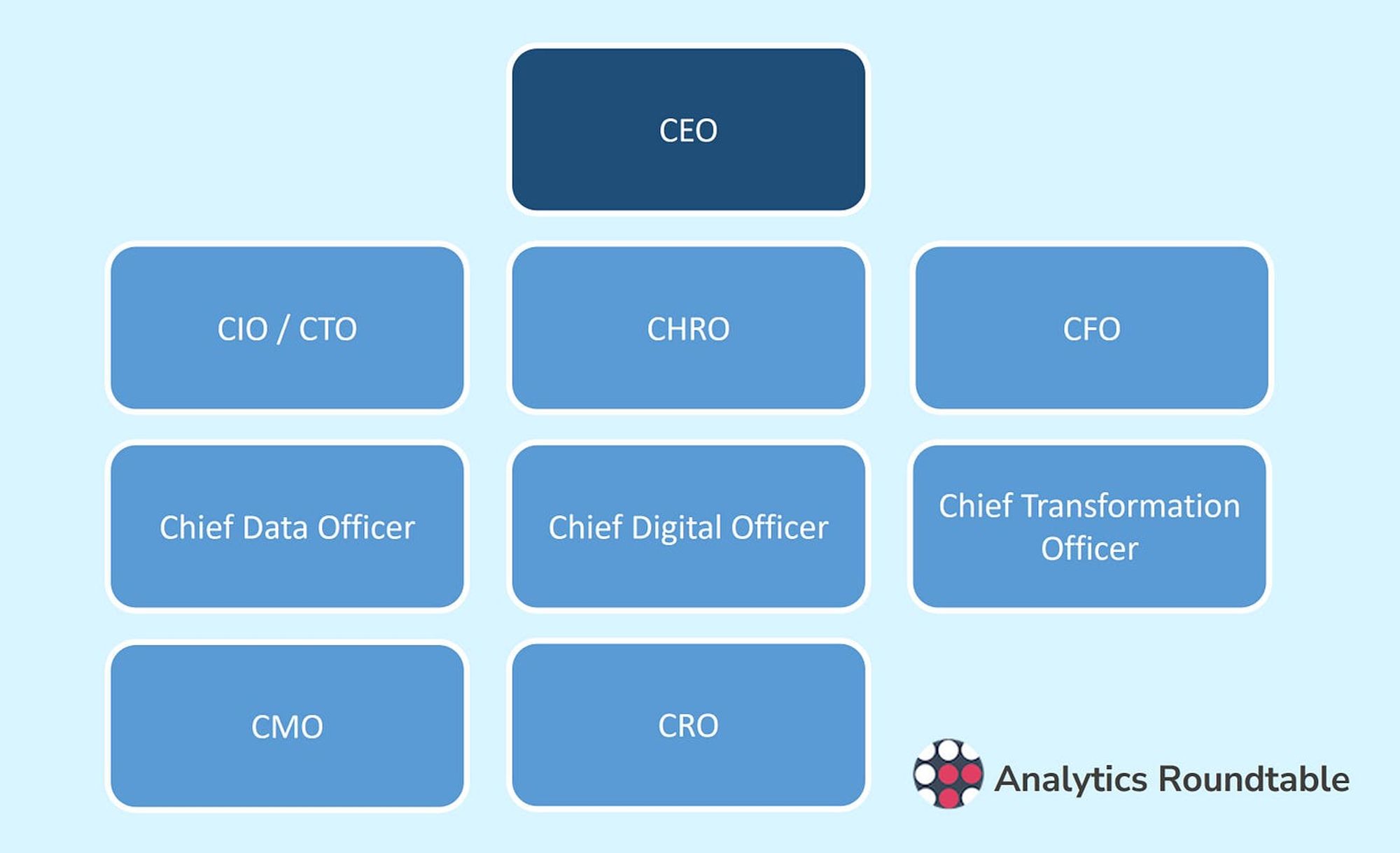
The ownership of the digital strategy can vary depending on the size and structure of the organisation. In some cases, the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) may be responsible for the digital strategy, particularly if it involves significant investments in technology or changes to the organisation’s financial processes.
In other cases, the Chief Digital Officer (CDO) may be responsible for the digital strategy, as they are often responsible for driving the organisation’s overall digital transformation efforts. The Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) may also have a role in developing the digital strategy, particularly if it involves marketing and customer engagement efforts.
The Chief Data Officer (CDO) may have a role in the development of the digital strategy, particularly if it involves the collection, management, and analysis of data. The CDO may be responsible for overseeing the organisation’s data assets and ensuring that they are being used effectively to support the business.
The Chief Information Officer (CIO) may also be involved in the development of the digital strategy, particularly if it involves the implementation of new technologies or the integration of digital systems across the organisation.
Ultimately, the person or team responsible for the digital strategy should have the necessary influence and authority to drive change across the organisation, as well as a deep understanding of the organisation’s goals, business model, and the competitive landscape.
What skills should someone have when owning the digital strategy?
There are a wide range of skills that can be helpful for someone who is responsible for owning the digital strategy of an organisation. Some key skills to consider include:
- Business acumen: It is important for the person responsible for the digital strategy to have a deep understanding of the organisation’s business model, goals, and competitive landscape.
- Strategic thinking: The person responsible for the digital strategy should be able to think strategically and develop a vision for how digital technologies can be leveraged to drive business value.
- Data analytics: The ability to collect, analyse, and interpret data is crucial for developing a successful digital strategy.
- Project management: The person responsible for the digital strategy should be able to manage projects effectively and ensure that the necessary resources and actions are in place to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Communication: The person responsible for the digital strategy should have strong communication skills and be able to effectively present and explain the strategy to a wide range of stakeholders.
- Leadership: The person responsible for the digital strategy should be able to inspire and lead others, and should be able to build and manage teams effectively.
- Adaptability: The person responsible for the digital strategy should be able to adapt to changing market conditions and technologies, and should be open to new ideas and approaches.
How do you overcome fear and resistance when executing a digital strategy?

Implementing a digital transformation strategy can be a complex and challenging process, and it is not uncommon for employees to experience fear and resistance when faced with change. Here are a few strategies that organisations can use to overcome fear and resistance when implementing a digital strategy:
- Communicate clearly and transparently: Employees may resist change if they feel that they are being kept in the dark or if they are not sure what is expected of them. By communicating clearly and transparently about the goals and objectives of the digital transformation effort, and by involving employees in the decision-making process, organisations can help to reduce fear and resistance.
- Provide training and support: Employees may be more likely to embrace change if they feel that they have the skills and knowledge they need to be successful. By providing training and support to employees, organisations can help them to feel more confident and prepared for the change.
- Foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement: By creating a culture that encourages employees to embrace change and take risks, organisations can help to reduce fear and resistance. This might involve creating a safe space for employees to experiment and learn from their mistakes, and recognising and rewarding employees who take on new challenges and contribute to the organisation’s success.
- Address concerns and address challenges: If employees are resistant to change, it is important to listen to their concerns and address any challenges they may be facing. By addressing these issues, organisations can help to build trust and reduce fear and resistance.
What are the success stories and can I learn more about them?
Here are a few success stories of organisations that have implemented digital transformation strategies:
- Amazon: Amazon has been a pioneer in the use of digital technologies to drive business growth. The company has used data and analytics to optimise its operations, improve the customer experience, and develop new products and services. One example of Amazon’s success is its use of predictive analytics to optimise its fulfillment center operations and improve delivery times for customers. Source.
- Unilever: Unilever, a global consumer goods company, has implemented a number of digital initiatives to improve the efficiency of its operations, increase transparency, and drive business growth. One example of Unilever’s success is its use of data and analytics to optimise its supply chain and reduce waste. Source.
- Johnson & Johnson: Johnson & Johnson, a leading healthcare company, has implemented a number of digital initiatives to improve the efficiency of its operations, increase transparency, and drive business growth. One example of J&J’s success is its use of data and analytics to optimise the performance of medical devices and improve patient outcomes. Source.
In Summary
Digital transformation is the process of using digital technologies to fundamentally change how an organisation operates and delivers value to its customers.
It is important because it allows organisations to improve efficiency, increase competitiveness, and drive business growth. To be successful, a digital transformation strategy should focus on data, models, and people.
To successfully execute digital transformation, organisations must define clear objectives, build a strong leadership team, foster a culture of innovation, and engage with customers and employees to maintain high engagement and input for change.
Digital transformation is a complex and ongoing process that requires careful planning and execution to be successful. It involves the adoption and integration of digital technologies such as data analytics, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence into all areas of the organisation, and can bring numerous benefits such as improving efficiency, increasing competitiveness, and driving business growth.
…
I hope you found this useful. I will be posting regularly so stay tuned. If you want additional content, check out Analytics Roundtable, to stay up to date with the latest technology and chat with others.
