
Digital transformation is a hot topic in the business world today, as more and more organisations seek to leverage the power of digital technologies to drive growth and improve efficiency. At its core, digital transformation is about using data, models, and people to fundamentally change how an organisation operates and delivers value to its customers.
Why is this important to understand?
Digital transformation is important because it allows organisations to leverage the power of digital technologies to fundamentally change how they operate and deliver value to customers. By embracing digital technologies, organisations can improve efficiency, increase competitiveness, and drive business growth.
Some specific ways in which digital transformation can be beneficial include:
- Improving customer experiences: Digital technologies can be used to create personalised, seamless experiences for customers, improving satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increasing efficiency: Digital technologies can help streamline business processes, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks and freeing up resources for other initiatives.
- Facilitating innovation: Digital technologies can enable organisations to experiment with new ideas and approaches, fostering a culture of continuous innovation.
- Enhancing collaboration: Digital tools can make it easier for teams to work together, regardless of location, improving communication and coordination.
- Enabling new business models: Digital technologies can enable organisations to create new products and services, or to deliver existing products and services in new and innovative ways.
- Enhancing security and compliance: By implementing digital technologies, organisations can improve their ability to protect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements.
We have seen various models, what is different about this one?
I have come across a variety of models that explain the six or seven stages of digital transformation, the ‘three amegos’ of digital transformation, and they are either too complex or they neglect the people and cultural change aspect of digital transformation.
It is important to simplify the approach to digital transformation because a complex and convoluted process can be difficult to understand and implement, and may result in delays or setbacks. A simplified approach can help to ensure that the process is more efficient and effective, and that it is easier for employees to understand and adopt.
The model that I will go into some detail on, looks at balancing three things; data, models and people.
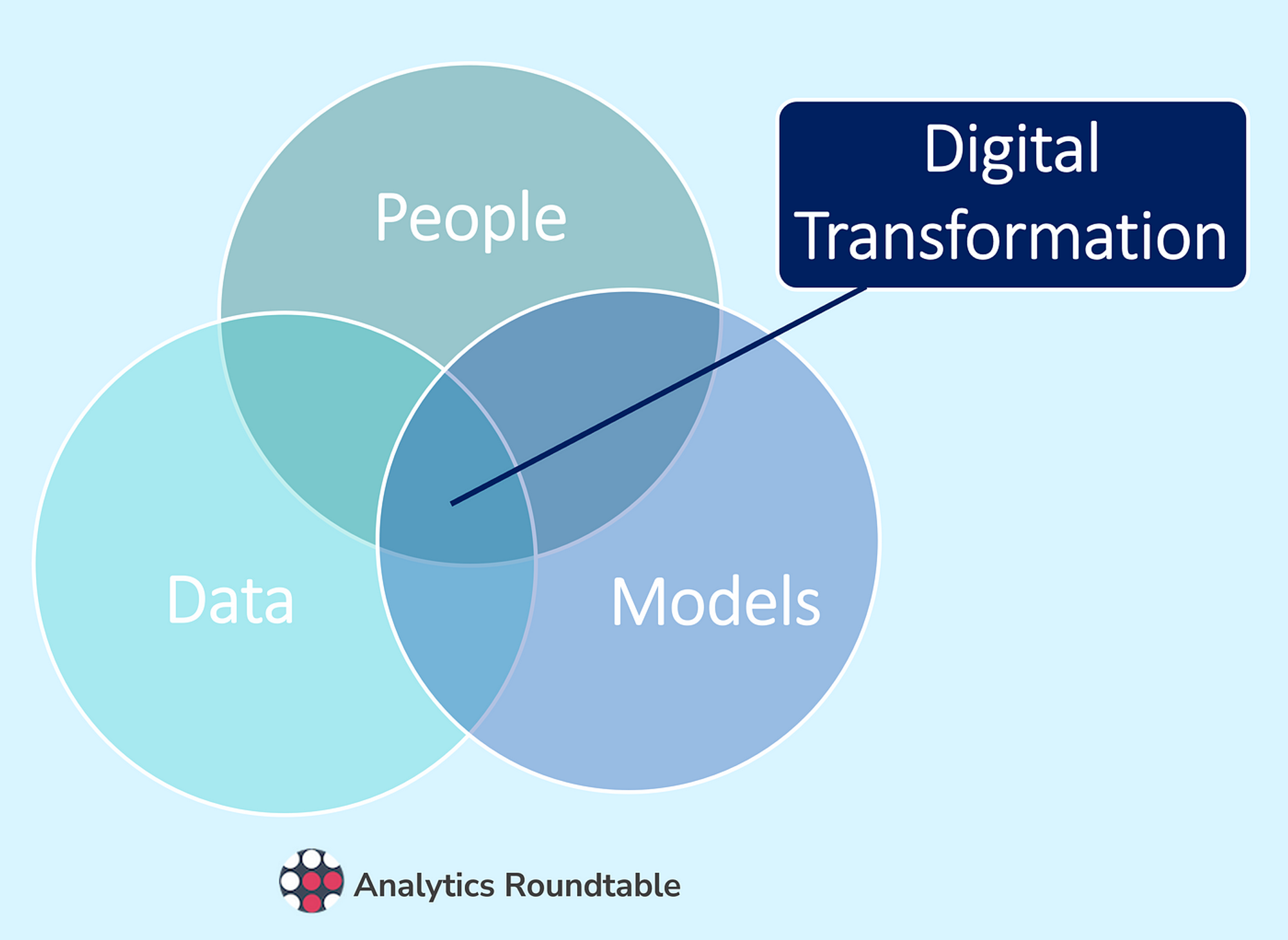
One key aspect of digital transformation is the use of data. By collecting and analysing data from a variety of sources, organisations can gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, as well as identify trends and patterns that can inform business decisions. This data can be used to drive the development of new products and services, optimise marketing efforts, and improve internal operations.
Models are another key element of digital transformation. By creating predictive models based on data, organisations can make informed decisions about the future and take proactive steps to optimise their operations. For example, a retailer might use data and models to forecast demand for certain products and adjust their inventory levels accordingly, or a healthcare provider might use data and models to predict patient outcomes and take preventative measures to improve health outcomes.
Finally, people are a crucial element of digital transformation. In order for digital transformation to be successful, organisations must have the right people in place to drive the change. This means having employees who are digitally literate and able to adapt to new technologies, as well as leaders who are able to envision and execute a digital strategy. It also means creating a culture that is open to change and innovation, and that encourages employees to embrace new technologies and ways of working.
Lets explore these in a little more detail with some examples;
Data
There are many types of data that can be used to drive business decisions about products and services. Some examples include:
- Customer data: This can include demographic information, purchasing history, and customer feedback. By analysing this data, organisations can understand the needs and preferences of their customers and use this information to inform product development and marketing efforts.
- Market data: This can include information about market trends, competitors, and industry benchmarks. By analysing this data, organisations can understand the larger market context in which they operate and make informed decisions about how to position their products and services.
- Sales data: This can include data on sales volume, revenue, and customer acquisition costs. By analysing this data, organisations can understand how their products and services are performing and make adjustments as needed to optimise sales.
- Operational data: This can include data on production costs, inventory levels, and supply chain efficiency. By analysing this data, organisations can identify opportunities to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Usage data: This can include data on how customers are using a product or service, including frequency of use and features that are most popular. By analysing this data, organisations can identify opportunities to improve the product or service and increase customer satisfaction.
Establishing processes to collect data and manage it is important
Establishing processes to collect data means creating a systematic and organised approach to gathering information. This can involve identifying the types of data that are needed, determining where and how to collect that data, and setting up processes to ensure that the data is collected in a consistent and reliable manner.
Having well-established processes for data collection is important because it helps to ensure that the data being collected is accurate and relevant, and that it can be used to inform business decisions. It also helps to streamline the data collection process and make it more efficient and secure.
Some examples of processes for collecting data might include:
- Setting up online surveys or polls to gather feedback from customers
- Tracking website traffic and user behavior through tools like Google Analytics
- Establishing protocols for collecting and storing data from sensors or other IoT devices
- Setting up systems to track sales and revenue data
- Implementing customer relationship management (CRM) systems to store and track data about customer interactions and purchases.
Maintaining relevance, privacy and security should underpin all data collection activities.
When organisations collect data from customers, they are essentially collecting personal information that belongs to those customers. It is important to respect this ownership and to handle the data in a responsible manner that respects the customers’ privacy and security. This includes ensuring that the data is only collected for relevant purposes, and that it is only used in ways that are consistent with the customers’ expectations and preferences.
Maintaining relevance, privacy, and security is also important because it helps to build trust and confidence in an organisation. Customers are more likely to trust an organisation that handles their data responsibly and protects their privacy and security. This can be especially important in industries where data privacy is a particularly sensitive issue, such as healthcare or financial services.
Relevance: Ensuring that the data being collected is relevant means that it is directly related to the purpose for which it is being collected. This helps to ensure that the data is useful and can be used to inform business decisions.
Privacy: Maintaining privacy means protecting the personal information of individuals and ensuring that it is not accessed or used without their consent. This is important because it helps to protect personal privacy and can help to maintain trust in an organisation.
Security: Ensuring the security of data involves protecting it from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This is important because it helps to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data, and can help to prevent data breaches and other security incidents.
Models
Models are important because they allow organisations to make predictions and decisions based on data. Models are essentially mathematical representations of real-world phenomena, and they can be used to understand complex systems and patterns, and to make informed decisions about the future.
There are many types of models that can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Statistical models: These models use statistical techniques to analyse data and make predictions about future outcomes.
- Machine learning models: These models use algorithms to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so.
- Simulation models: These models use computer algorithms to simulate real-world systems and predict how they will behave under different conditions.
- Optimisation models: These models use mathematical techniques to identify the best possible solution to a problem, given certain constraints and objectives.
In isolation, models can be limited because they are based on the data and assumptions that are used to create them. If the data is incomplete or biased, or if the assumptions are not accurate, the model may produce inaccurate or misleading outputs.
This is why establishing processes to improve organisational knowledge is important. By actively seeking out and incorporating new information and insights, organisations can improve their understanding of the models and the systems they are trying to understand. This can help to identify potential limitations in the models and to take steps to address them.
- Providing context: Organisational knowledge can help to provide context for the models and their outputs, making them easier to interpret and understand. For example, if a model is being used to predict customer behavior, organisational knowledge about the company’s customers, products, and market can help to provide insight into why the model is producing certain outputs.
- Identifying potential biases: Organisational knowledge can also help to identify potential biases in the models and their outputs. For example, if the data used to train a model is not representative of the population, the model may produce biased outputs. Organisational knowledge can help to identify these biases and take steps to address them.
- Enhancing decision-making: By understanding the models and their outputs, organisations can use this knowledge to inform their decision-making. For example, if a model is being used to predict future demand for a product, understanding the model’s outputs can help the organisation to make informed decisions about how much of the product to produce and how to allocate resources.
People
People are important to the process of digital transformation because they play a crucial role in driving change and adopting new technologies and ways of working. Without the right people in place, digital transformation efforts can be difficult to implement and sustain.
Some specific ways in which people are important to the process of digital transformation include:
- Leadership: Strong leadership is essential for envisioning and executing a digital transformation strategy. Leaders must be able to articulate a clear vision for the future and to inspire and guide employees through the change process.
- Digital literacy: Digital transformation requires employees to be digitally literate and able to adapt to new technologies and ways of working. Having a workforce with strong digital skills is essential for driving innovation and enabling the organisation to take advantage of new technologies.
- Cultural change: Digital transformation often requires organisations to fundamentally change their culture and ways of working. This requires employees to be open to change and innovation, and to be willing to embrace new technologies and approaches.
Weakness in the area of people and culture can result in a number of challenges during the process of digital transformation. Specific examples include;
- Efforts being focused in the wrong direction: If there is a lack of clear leadership or vision, or if employees are not aligned with the goals of the transformation, efforts may be misdirected or ineffective.
- Insights being translated incorrectly: If employees do not have the necessary skills or knowledge to understand and interpret data and insights, they may draw incorrect conclusions or make inappropriate decisions.
- Advanced specialist teams finding it difficult to drive value from their efforts: If employees do not have the necessary skills or cultural mindset to adopt and utilise new technologies, these teams may struggle to drive value from their efforts. This can lead to frustration a lack of progress, and your competitors gaining the edge.
In Summary
Digital transformation is a process that involves using digital technologies to fundamentally change how organisations operate and deliver value to customers. It requires the integration of data, models, and people in order to be successful.
Data is a key element of digital transformation, as it allows organisations to gather and analyse information in order to inform business decisions. Models are used to make predictions and decisions based on data, while people are essential for driving change and adopting new technologies and ways of working.
Here are a few articles that I have found helpful
- “The 7 Elements of Digital Transformation” by Forbes discusses the key elements that organisations need to consider when embarking on a digital transformation journey.
- “Unlocking success in digital transformations” by McKinsey provides a framework for planning and executing a successful digital transformation.
- “Democratizing Transformation” by the Harvard Business Review discusses the role of data in driving transformation and provides guidance on how to successfully scale data-driven initiatives.
- “Digital transformation has evolved. Here’s what’s new” by MIT Sloan Management Review discusses the importance of cultural change and employee engagement in digital transformation, and offers strategies for building a culture that is supportive of innovation.
Overall, the integration of data, models, and people is essential for successful digital transformation. By leveraging these elements effectively, organisations can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and increase competitiveness.
…
I hope you found this useful. I will be posting regularly so stay tuned. If you want additional content, check out Analytics Roundtable, to stay up to date with the latest technology and chat with others.

Are you competing with analytics?
Here is a useful ‘competing with analytics’ checklist

Surviving Digital Transformation
Digital transformation will only grow in importance as we enter the near year as it allows organisations to leverage the power of digital technologies to fundamentally change how they operate and deliver value to customers.